200以上 bacterial sinusitis sinusitis treatment antibiotics 131171-How to treat a bacterial sinus infection
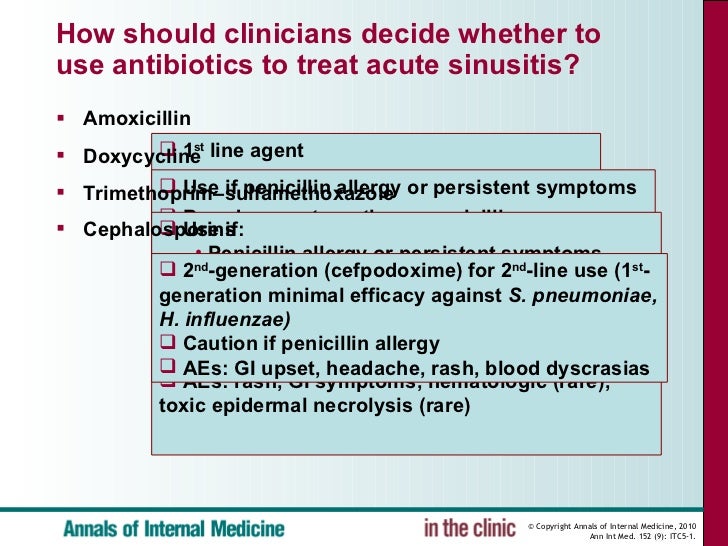
If antibiotics are needed, amoxicillin, with or without clavulanate, for five to 10 days is recommended as firstline therapy Amoxicillin is inexpensive, and clinical trial results show it's as effective as costlier cephalosporins A detailed algorithm further clarifies the diagnosis and treatment of adult sinusitisAntibiotic Treatment IS Indicated for Pediatric Patients Diagnosed With ABS High Risk Patient Exclusion Upper Respiratory Symptoms Less Severe Assess Pediatric Patient for Acute Bacterial Sinusitis (ABS) • Third line antibiotics include the following for 1014 day therapy Cefdinir (Omnicef) 14 mg/kg/day PO taken once daily or the dose can beFrom bacterial acute sinusitis The risk for bacterial sinusitis is low until the symptoms persist for at least 7 to 10 days A Cochrane review of 57 randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) from 1950 to 07 of antibiotics in the treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis reported that antibiotic treatment reduced

Sinusitis And Rhinitis Ent And Dental Emergencies Harwood Nuss Clinical Practice Of Emergency Medicine 6 Ed
How to treat a bacterial sinus infection
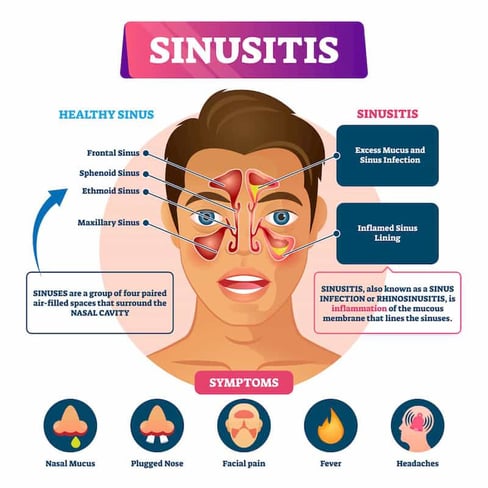
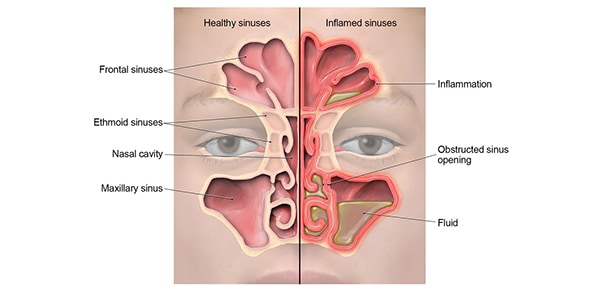
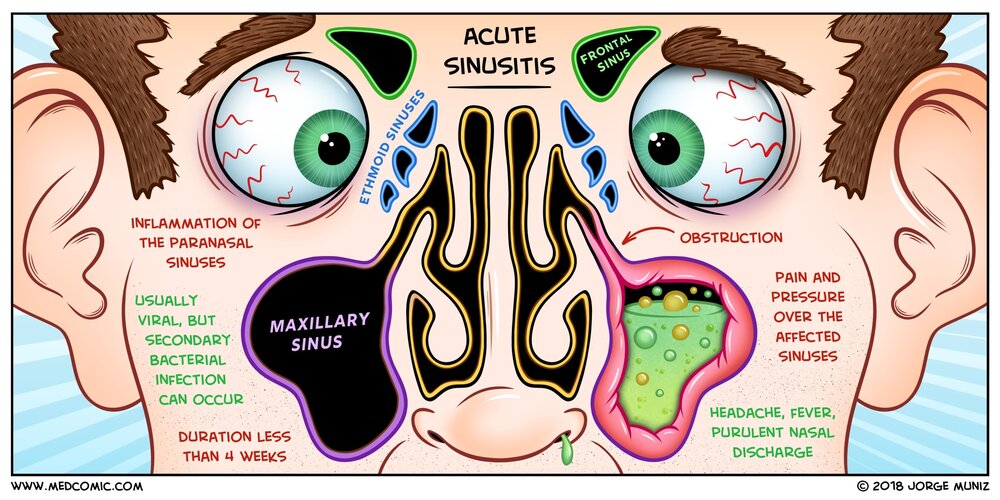
How to treat a bacterial sinus infection-Several practice guidelines for the treatment of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis have been published in the US within the past decade (3, 6, 7, 33, 59, 63, , 97) These guidelines present varying opinions about the clinical criteria for initiation and choice of empiric antimicrobial regimensSinusitis is an inflammation, or swelling, of the tissue lining the sinuses The sinuses are four paired cavities (spaces) in the head They are connected by narrow channels The sinuses make thin mucus that drains out of the channels of the nose This drainage helps keep the nose clean and free of bacteria



1
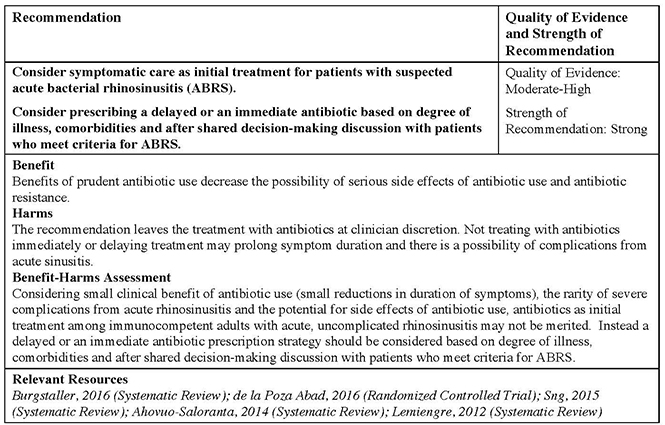
treatment, regardless of cause (bacteria or virus) • Antibiotics are not needed for most people The number of people improving with antibiotics is similar to the number getting adverse effects, such as diarrhoea • Complications of acute sinusitis are rare (about 25 to 43 per million people per year)Sinusitis affects about 1 in 8 adults in the United States, resulting in over 30 million annual diagnoses 3,4 The direct cost of managing acute and chronic sinusitis exceeds $11 billion per year, 4,5 with additional expense from lost productivity, reduced job effectiveness, and impaired quality of life 68 More than 1 in 5 antibioticsAntibiotics are indicated for sinusitis that is thought to be bacterial, including sinusitis that is severe or involves the frontal, ethmoid, or sphenoid sinuses, since this type of sinusitis
Background For adults seeking care in ambulatory medical practices, sinusitis is the most common diagnosis treated with antibiotics Objectives We examined whether antibiotics are indicated for acute sinusitis, and if so, which antibiotic classes are most effective Search strategy Relevant studies were identified from searches of MEDLINE and EMBASE in December 01, contacts withSinuses and Antibiotics Patients with painful sinus problems often plead with their doctors to give them an antibiotic ASAP About 90% of adults seen in the US by aAntibiotics are medications derived from naturally occurring chemicals produced by bacteria and molds to inhibit the growth of competing microorganisms Penicillin was discovered in 1929 by Alexander Fleming and its popular derivative amoxicillin remains effective for 80% of acute bacterial sinus infections and 99% of strep throat infections
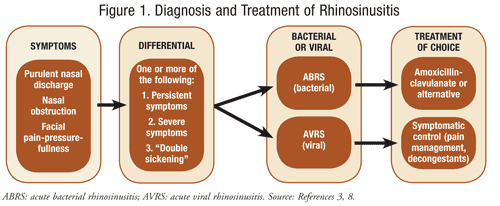
Background Sinusitis is usually defined as an acute bacterial infection involving the mucosal surfaces of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity 1,3,9 It usually occurs secondary to an upper respiratory tract infection, but may develop from several other causes including swimming in contaminated water, the introduction of a nasal foreign body, or an ascending dental infection 9(2) decrease the duration of symptoms to allow patients to resume daily activities more quickly;The primary goal of antibiotic therapy is to eradicate bacteria from the site of infection, which, in turn, helps (1) return the sinuses back to health;



1




Comparison Of Antibiotics With Placebo For Treatment Of Acute Sinusitis A Meta Analysis Of Randomised Controlled Trials The Lancet Infectious Diseases
If your sinusitis is viral, the best treatment is usually plenty of rest and drinking fluids to help thin the mucus You can also take decongestants to help clear your sinuses, but they'll heal on their own with time as the virus runs its course In contrast, bacterial sinusitis can require antibiotics in order to fight off the bacteria thatSinus pain, fever, sinus tenderness on exam, and purulent pharyngeal discharge have not been shown to be useful in acute bacterial rhinosinusitis diagnosis7 TABLE Clinical prediction rule for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis Symptoms PPV Local pain, unilateral sinus pain for 48 hours, presence of pus under rhinoscopy Main exclusion criteria Symptoms 1 month Antibiotics duringTrimethoprim (Bactrim) – This drug is the brand name for a medication that is a combination of two antibiotics trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole that is used to treat bacterial infections Bactrim works by preventing the growth of bacteria These antibiotics are effective in treating sinus infection, however, these drugs do carry side effects




Recommendations For Initial Use Of Antibiotics For Acute Bacterial Download Table



2
Most cases of sinusitis clear up within 10 days Antibiotics are not needed for acute viral sinusitis If a secondary bacterial infection should develop, one treatment of choice is amoxicillinclavulanate (Augmentin) In patients who have severe allergy to penicillintype drugs, doxycycline is a reasonable alternativeAntibiotic therapy for acute bacterial sinusitis is indicated in children with severe onset or worsening course Either antibiotic therapy or additional observation is recommended for 3 days to children with stable illness Amoxicillin with or without clavulanate is the firstline treatment of acute bacterial sinusitisA sinus infection, aka sinusitis, can be either a viral or bacterial infection The term "sinusitis" simply means that there's irritation in your sinuses, which make up the lining around



6 Common Symptoms Of Chronic Sinusitis



Sinus Infection Sinusitis
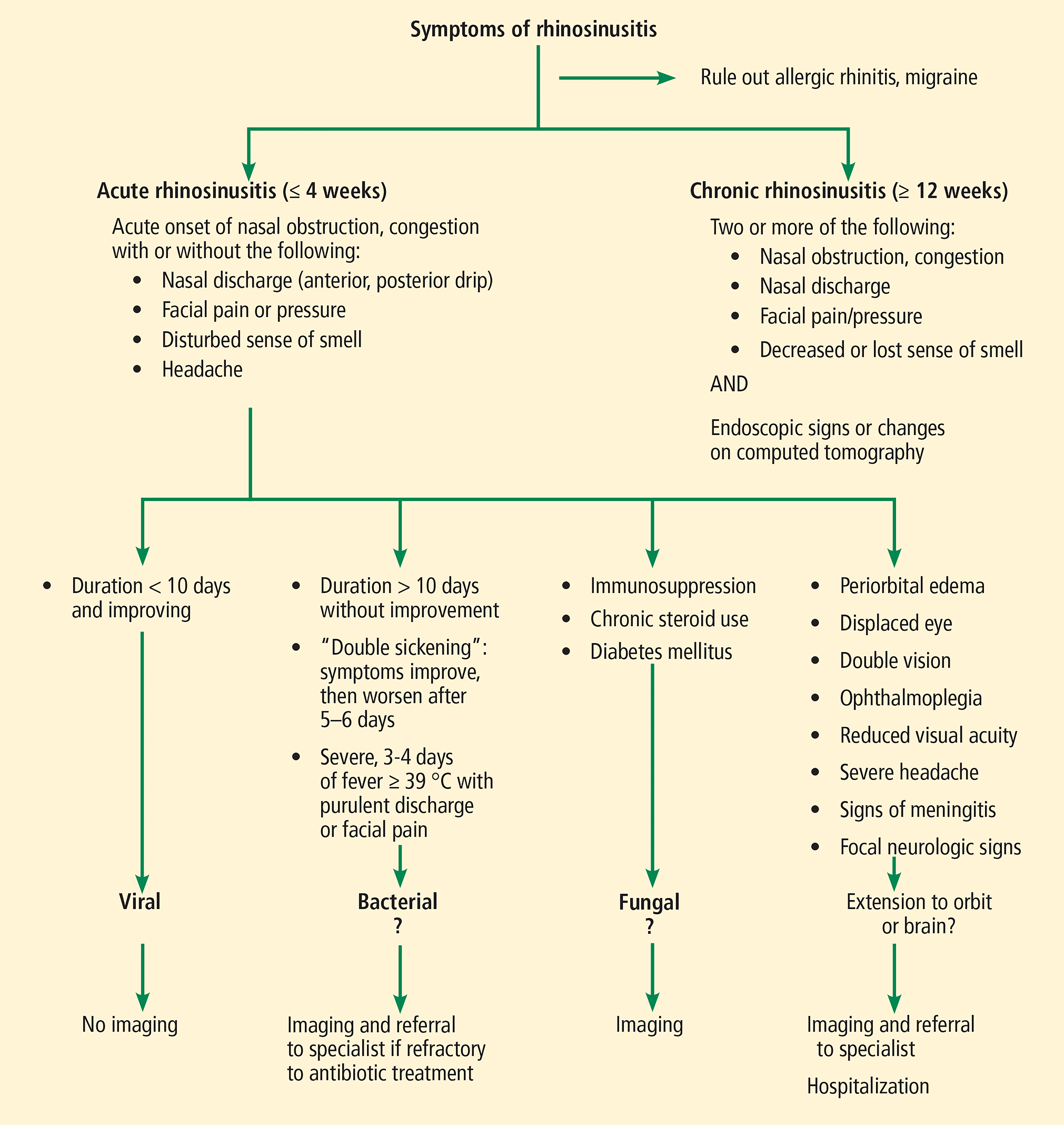
Treatments for ABRS can include Antibiotics to kill the infecting bacteria Pain medicines Rinsing the nasal passages with saline to make them feel betterInflammation in the sinuses can cause a runny nose, greenish and yellowish mucous production, and even pain But these symptoms do not mean that you have a bacterial sinus infection Certainly a bacterial sinus infection would benefit from an antibiotic But did you know that 9 out of 10 sinus infections are actually caused by viruses?Think Twice about Antibiotics for Acute Bacterial Sinusitis Adult With Possible Sinusitis Duration ≤ 4 Weeks Duration >




Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis Springerlink



An Overview Of The Treatment And Management Of Rhinosinusitis
Treatment Patients presenting with symptoms for around 10 days or less, should be given advice about the usual duration of acute sinusitis, selfcare of pain or fever with paracetamol or ibuprofen, and when to seek medical helpPatients should be reassured that antibiotics are usually not required Some patients may try nasal saline or nasal decongestants, however there is limitedAntibiotics are not needed for many sinus infections Most sinus infections usually get better on their own without antibiotics When antibiotics aren't needed, they won't help you, and their side effects could still cause harmAcute sinusitis is usually caused by a virus and is only complicated by bacterial infection in about 2 in 100 cases It takes 2–3 weeks to resolve, and most people will get better without antibiotics Symptoms, including fever, can be managed with selfcare measures such as paracetamol or ibuprofen for pain or fever



1000




Ppt Acute Sinusitis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
And (4) decrease the development of chronic diseaseIn a survey of chronic rhinosinusitis treatment in children by pediatric primary care, pediatric otolaryngology, and pediatric urgent care providers, Newton et al reported that 21% of the otolaryngology providers prescribed antibiotic therapy for 7 days past any symptom, compared with 6% and 5% of the primary care and urgent care providers12 Weeks Duration ≥ 12 Weeks *Requires assurance of followup If penicillin allergy prescribe doxycycline or a respiratory quinolone **Failure to improve by 7 days after diagnosis or worsening at any time




Pediatric Sinusitis Diagnosis Management Criteria Grepmed



Acute Sinusitis Treatment Icsi
Amoxicillinclavulanate is often prescribed for a bacterial sinus infection Depending on the type of antibiotic, they may be taken from 3 to 28 daysAntibiotics for the treatment of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis are outlined in Table 2 Most guidelines recommend amoxicillin with or without clavulanate as a firstline antibiotic for adults because of its safety, effectiveness, low cost, and narrow microbiologic spectrum 39)Factors Influencing Treatment Decisions for Acute Sinusitis Many experts in the management of acute sinusitis have stressed that the diagnosis of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis (ABRS) is being made too frequently, with accompanying excessive prescription of oral antibiotics




Sinusitis And Rhinitis Ent And Dental Emergencies Harwood Nuss Clinical Practice Of Emergency Medicine 6 Ed




Sinus Infections Causes Symptoms Natural Support Strategies Sinus Infection Remedies Sinusitis Sinusitis Treatment
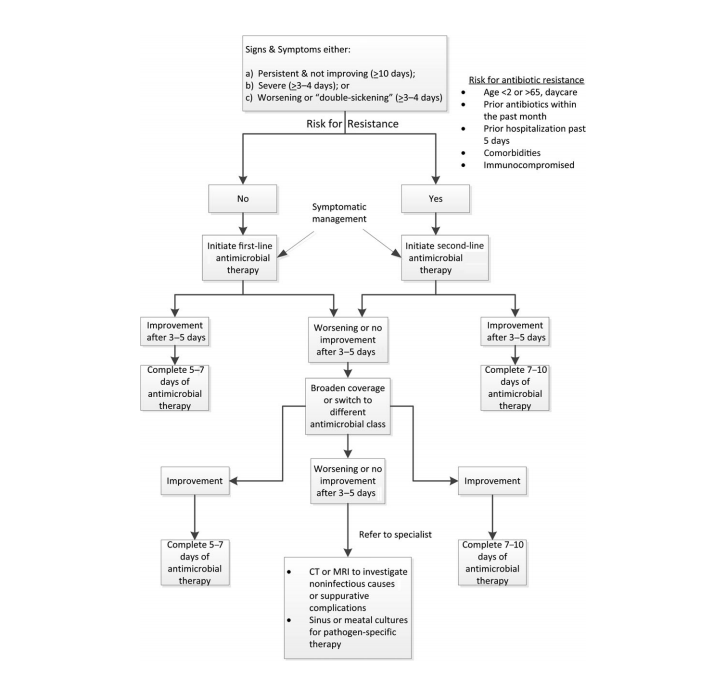
The IDSA guidelines recommend 5–7 days of antibiotics for adult bacterial sinusitis, rather than the 10–14 days in previous guidelines, to discourage development of resistance Importantly, the new guidelines suggest treatment with amoxicillinclavulanic acid instead of the current standard of amoxicillin aloneManagement Antibiotics Precautions Premature antibiotic use (and Antibiotic Overuse) in Acute Sinusitis is common and unwarranted Up to 70% of Acute Sinusitis <14 days resolves without antibiotics Number Needed to Treat (NNT) for antibiotic in Acute Sinusitis benefit 1115However, amoxicillinclavulanate had significantly more dropouts due to adverse effects than cephalosporins and macrolides (AhovuoSaloranta, 14) The ICSI work group did not specifically search for primary literature on firstline vs alternative antibiotic treatments



1




Ppt Acute Sinusitis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Antibiotics should be prescribed for adults for preventing serious complications or speeding up the recovery process only if the diagnosis confirms that the patient is suffering from an acute bacterial sinus infectionAntibiotic treatment becomes necessary for adults if the following symptoms are observedAntibiotics are currently used in % of children with acute sinusitis, although the majority of these infections would likely resolve on their own 11 However, when controlled for symptoms that suggest a diagnosis of acute bacterial sinusitis, antibiotics are associated with a higher cure rate (50% vs 14%) and lower treatment failure (14% vsTreatment With Antibiotics There are some circumstances in which antibiotics work to eliminate sinus infections, such as by fighting bacterial sources But when a sinus infection is caused by allergies, a virus, or other causes such as a structural defect of the sinuses, an antibiotic will not help to alleviate symptoms




Rhinosinusitis Jihan Al Maddah Definition Inflammation



Sinus Infection Sinusitis Antibiotic Use Cdc
Antibiotics for the treatment of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis are outlined in Table 3 Most guidelines recommend amoxicillin with or without clavulanate as a firstline antibiotic for adults because of its safety, effectiveness, low cost, and narrow microbiologic spectrum 52)Acute sinusitis is one of many medical disorders that can be caused by a bacterial infection However, it is important to remember that colds, allergies, and environmental irritants, which are more common than bacterial sinusitis, can also cause sinus problems Antibiotics are effective only against sinus problems caused by a bacterial infectionIf the diagnostic criteria are strict, acute bacterial sinusitis should be treated with antibiotics as they are significantly more effective than placebo alone 6 Amoxycillin is still considered firstline treatment




Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis In Adults Part Ii Treatment American Family Physician



Acute Sinusitis
Acute sinusitis is typically a shortterm condition that is not too severe For many people, little or no treatment is needed Most people get better on their own after seven to 10 days Antibiotics are only helpful for bacterial infections Most sinusitis is due to viruses or other causes that are not cured by antibiotics(3) prevent severe complications such as meningitis and brain abscess;Bacterial sinusitis is less common than viral sinusitis and requires antibiotics, while viral sinusitis is most common and does not require antibiotics Fungal sinusitis is




Nice Sinusitis Acute Antimicrobial Prescribing Nice Guideline Guidelines



Is Your Sinus Bothering You Treatment Of Sinusitis And Tips For Prevention Infographic



Acute Bronchitis And Rhinosinusitis Perspectives From Antimicrobial Stewardship



2



Antibiotics For Sinus Infection Dental Science




Figure 5 From Medical Management Of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis Recommendations Of A Clinical Advisory Committee On Pediatric And Adult Sinusitis Semantic Scholar




Sinusitis Ear Nose And Throat Disorders Msd Manual Professional Edition




Sinusitis Ear Nose And Throat Disorders Msd Manual Professional Edition




Acute Sinusitis And Antibiotic Treatment British Journal Of General Practice



Sinusitis




Acute And Chronic Sinusitis And Allergies




Acute Bacterial Sinusitis



1



Www Stonybrookmedicine Edu Sites Default Files Sinusitis Pdf




Stewardship In The Pediatrician S Office Antibiotic Use For Acute Sinusitis




Adult Acute Rhinosinusitis The Bmj



Http Www Just Edu Jo Dic Clinicguidlines Acute sinusitis and rhinosinusitis Pdf




Introduction To Sinus




Pharmahubng Nasal Health What Is A Sinus Infection Or Sinusitis Inflammation Of The Air Cavities Within The Passages Of The Nose Paranasal Sinuses Is Referred To As Sinusitis Sinusitis Can




Figure Algorithm For Use Of Antibiotics In Acute Sinusitis Msd Manual Professional Edition



2
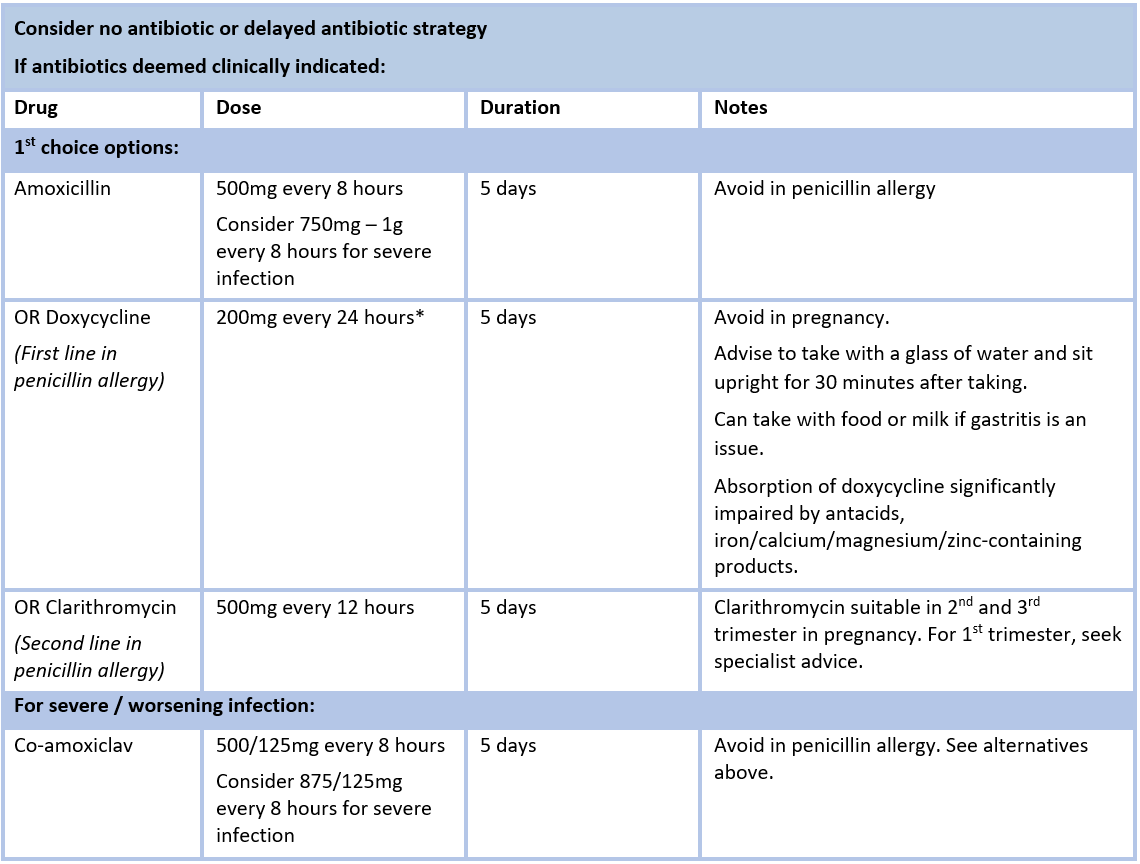



Acute Sinusitis Adults Delayed Antibiotic Strategy Hse Ie
/sinusitis-symptoms-5ae0c1c118ba010037db3f29.png)



Signs Symptoms And Complications Of Sinus Infections



Www Ajol Info Index Php Cme Article View 274




Parameters For The Diagnosis And Management Of Sinusitus Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology




Current Concepts In Adult Acute Rhinosinusitis American Family Physician




Acute And Chronic Sinusitis Ppt Download




Nice Sinusitis Acute Antimicrobial Prescribing Nice Guideline Guidelines



Are You Using The Correct Treatment For Your Sinusitis Health24




Acute Sinusitis In Adults Nejm



2




Canadian Guidelines For Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada




Acute Rhinosinusitis In Adults American Family Physician




Recommendations For Initial Use Of Antibiotics For Acute Bacterial Download Table




Acute Rhinosinusitis In Adults American Family Physician




In The Name Of God Sinusitis Sinusitis Is
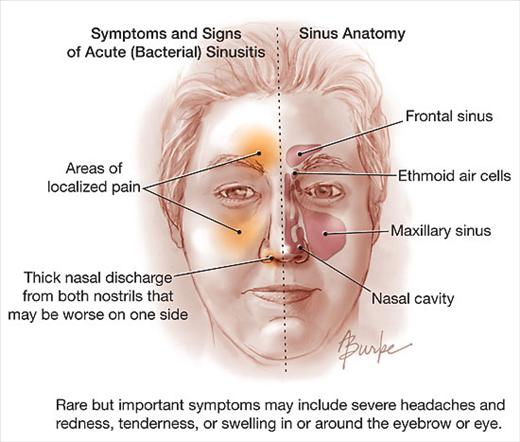



Acute Rhinosinusitis Core Em



Http Www Just Edu Jo Dic Clinicguidlines Acute sinusitis and rhinosinusitis Pdf




Emergency Department Sinusitis Care Simplified Page 2 Of 2 Acep Now Page 2




Sinusitis Archives Columbus Indiana



Http Www Sienapediatrics Com Sinusitis Pdf



Acute Sinusitis Medcomic



Www Gacguidelines Ca Site Gac Guidelines Assets Pdf Sinu Adul06 Summary Pdf




Chronic Rhinosinusitis And Nasal Polyposis Ppt Video Online Download



2



Http Eqipp p Org File library Courses Judicioususe Antibioticsuseflowchart Abs Final Pdf




Acute Rhinosinusitis In Adults American Family Physician




Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis Patient Assessment Risk Stratification Referral Strategies And Outcome Effective Antibiotic Selection Part I 04 04 19 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing




Clinical Practice Guideline Management Of Sinusitis American Academy Of Pediatrics



Plos One High Dose Versus Standard Dose Amoxicillin Clavulanate For Clinically Diagnosed Acute Bacterial Sinusitis A Randomized Clinical Trial



Intermountainhealthcare Org Ckr Ext Dcmnt Ncid



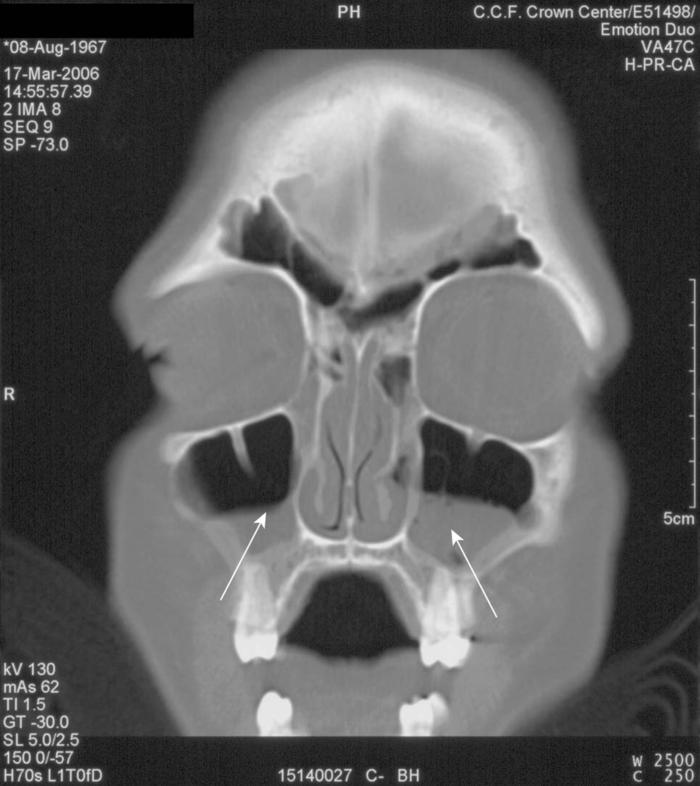
Rhinosinusitis And The Role Of Imaging Cleveland Clinic Journal Of Medicine



2
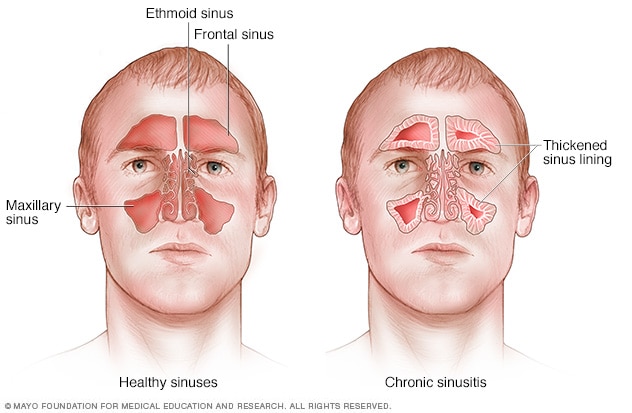



Chronic Sinusitis Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic




Sinus Infection Sinusitis Symptoms Treatment Causes Narayana Health



Printout Acute Sinusitis Therapy



Sinusitis Medical Services Services Musc Health Charleston Sc




Sinusitis Springerlink



Sinusitis




Acute Sinusitis In Adults Nejm Resident 360 Meta Property Twitter Image Content Resident360files Nejm Org Image Upload C Fit F Auto H 1 W 1 V U8buf4o8mgdxgmfcczjk Png Meta Property Og Image Content




Main Therapeutic Options On Acute Bacterial Download Table



2




Xmlinkhub



2




Sinusitis




Table 1 From Clinical Practice Acute Sinusitis In Adults Semantic Scholar




Fluoroquinolones Compared With B Lactam Antibiotics For The Treatment Of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis A Meta Analysis Of Randomized Controlled Trials Cmaj



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177




Acute Sinusitis In Adults Nejm



Printout Acute Sinusitis Therapy




Figure 4 From Medical Management Of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis Recommendations Of A Clinical Advisory Committee On Pediatric And Adult Sinusitis Semantic Scholar
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SinusInfectionRemedies_1191989_Final_1-b1ba1a6e6dfd456487524707c668bcd1.jpg)



How Sinus Infection Is Treated



Qpp Cms Gov Docs Qpp Quality Measure Specifications Cqm Measures 19 Measure 331 Mipscqm Pdf



Acute Rhinosinusitis Core Em
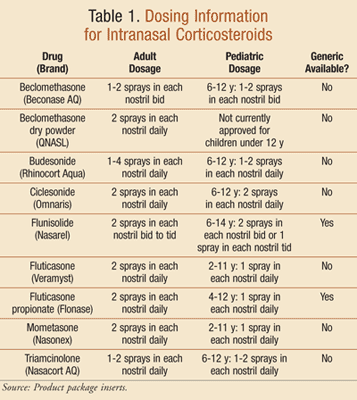



An Overview Of The Treatment And Management Of Rhinosinusitis




Antibiotics Do S And Don Ts Wsj
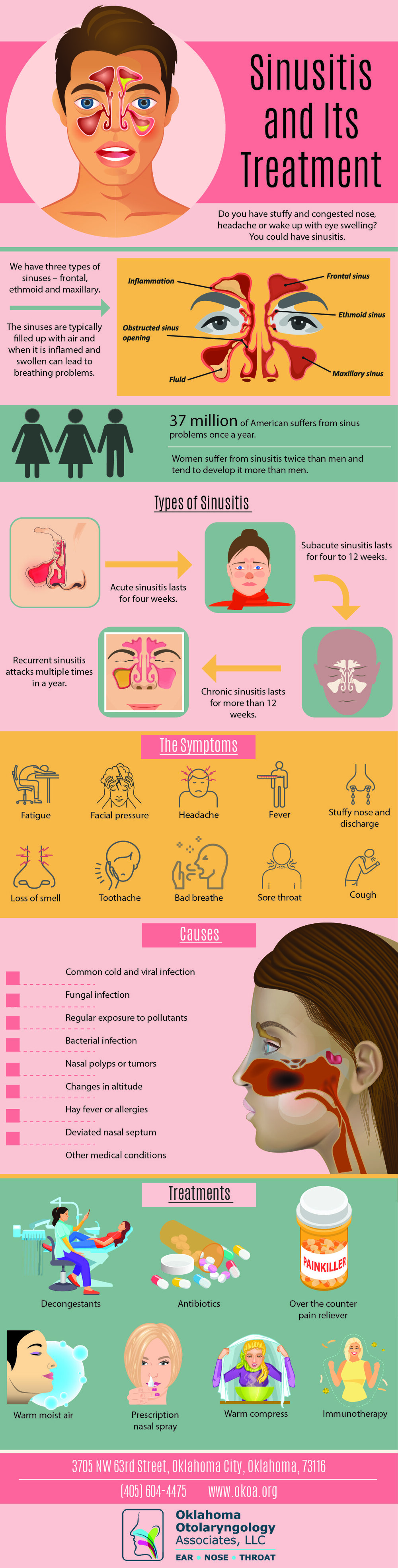



Sinusitis Treatment Articles



Doh Sd Gov Documents Diseases Hai Pediatricacutebacterialsinusitis Pdf




Acute Rhinosinusitis In Adults American Family Physician
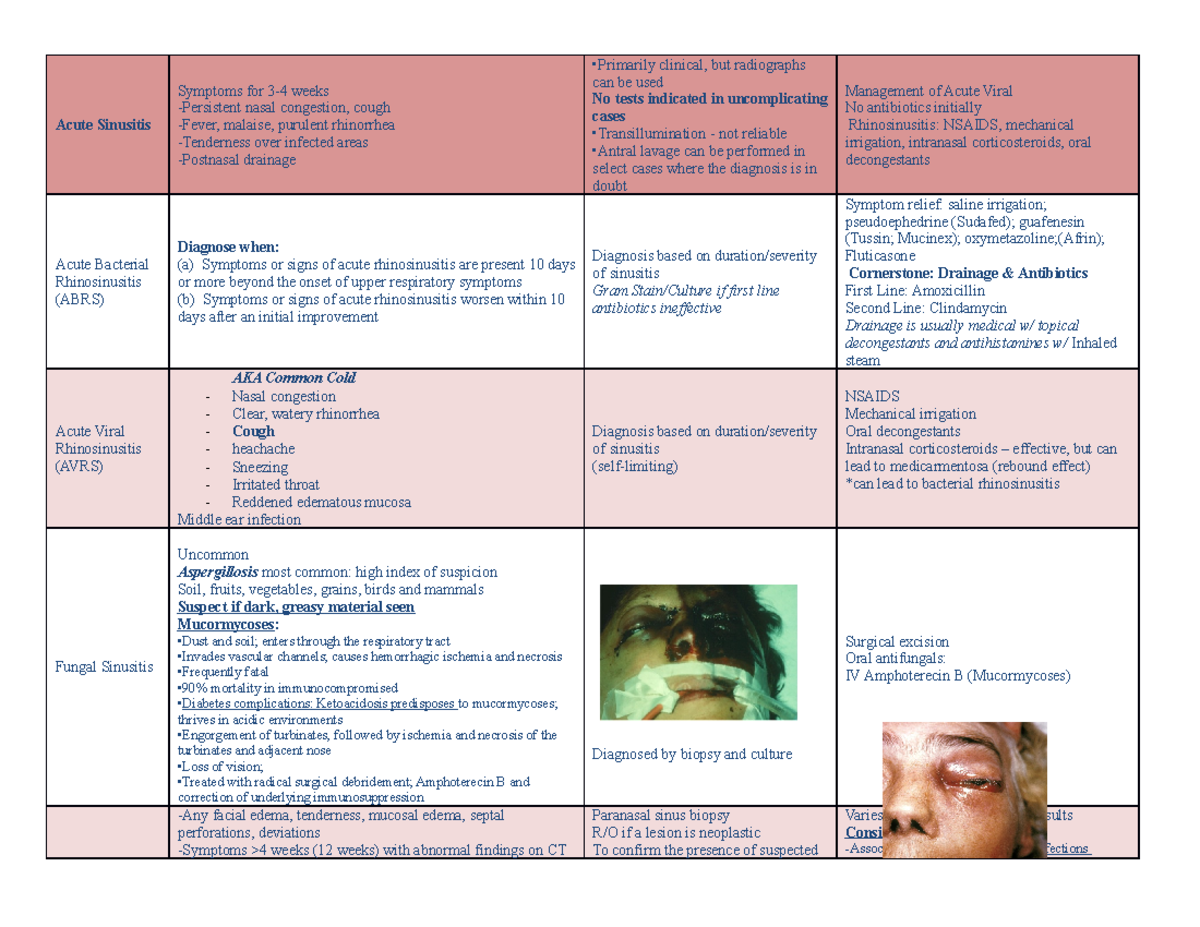



Heent Chart For Final Lecture Notes Everything Acute Sinusitis Symptoms For Weeks Persistent Nasal Congestion Cough Fever Malaise Purulent Rhinorrhea Studocu



Static Cigna Com Assets Chcp Pdf Resourcelibrary Medical Commit2quality Sinusitis Acute Pdf




1 8 Sinusitis And Antibiotics Part Ii Exercise 1 2 Chegg Com



Introduction To Sinus




The Diagnosis And Management Of Sinusitis A Practice Parameter Update Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology


コメント
コメントを投稿